本文最后更新于:December 3, 2021 pm
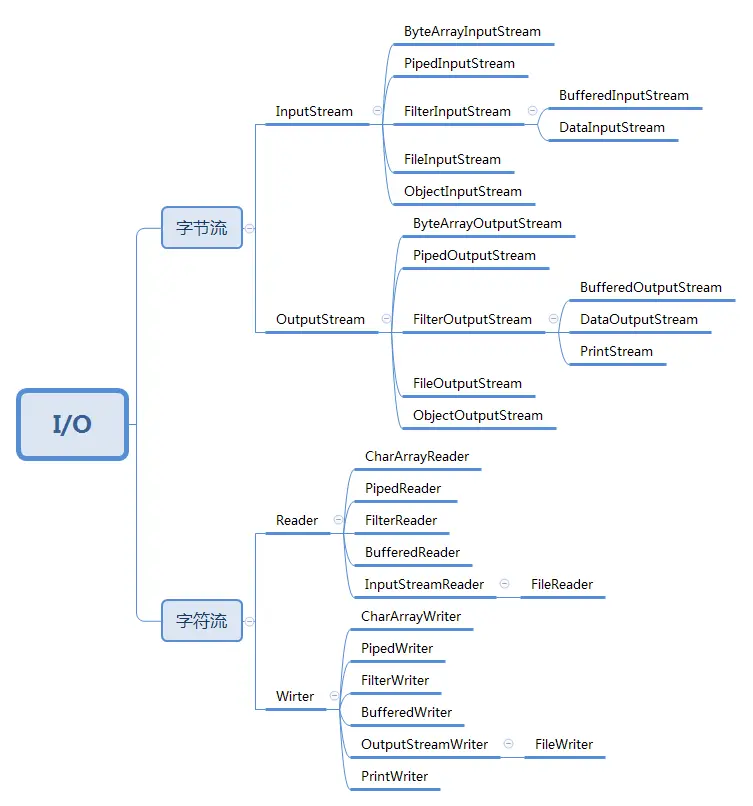
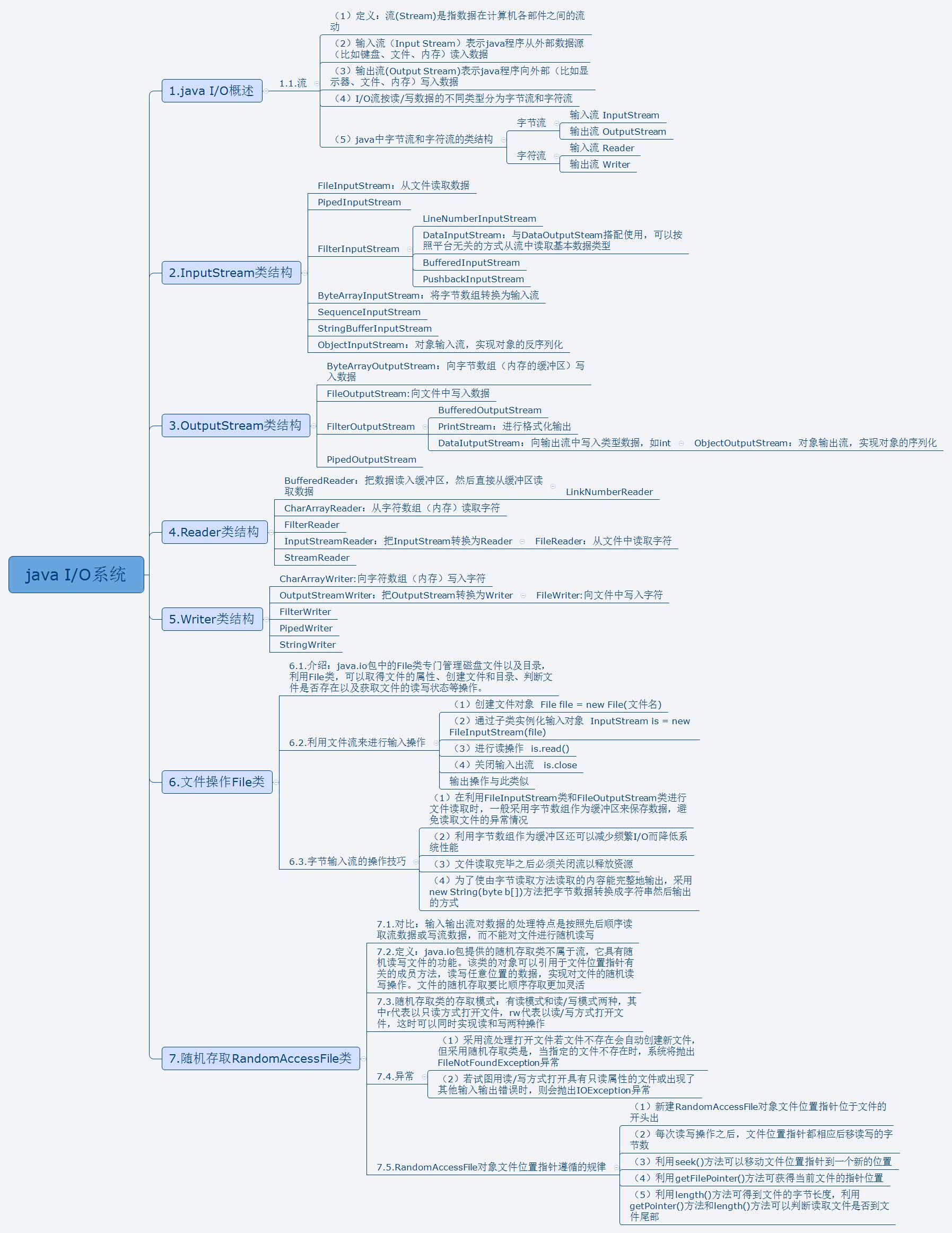
Java的核心库java.io提供了全面的IO接口。包括:文件读写、标准设备输出等。Java中IO是以流为基础进行输入输出的,所有数据被串行化写入输出流,或者从输入流读入。在整个Java.io包中最重要的就是5个类和一个接口。5个类指的是File、OutputStream、InputStream、Writer、Reader;一个接口指的是Serializable。
目录
1.IO流 1.1 分类
按方向
输入流:将 存储设备 中的内容读入到 内存 中。
输出流:将 内存 中的内容写入到 存储设备 中。
按单位
字节流:以字节为单位,可以读写所有数据 。
字符流:以字符为单位,只能读写文本数据。
按功能
节点流:具有实际传输数据的读写功能。
过滤流:在节点流的基础之上增强功能。
2.字节流 字节流的父类为抽象类。
InputStream就是Java标准库提供的最基本的输入流。它位于java.io这个包里。java.io包提供了所有同步IO的功能。InputStream并不是一个接口,而是一个抽象类,它是所有输入流的超类。这个抽象类定义的一个最重要的方法就是int read()。这个方法会读取输入流的下一个字节,并返回字节表示的int值(0~255)。如果已读到末尾,返回-1表示不能继续读取了。
int read():从该输入流读取一个字节的数据。返回字节的ASCII码。
int read(byte[] b):从该输入流读取最多 b.length个字节的数据为字节数组。返回读取的字节数。
int read(byte[] b, int off, int len):从该输入流读取最多 len字节的数据为字节数组。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 public static void main (String[] args) throws Exceptionnew FileInputStream("src/main/java/com/IO/dataTeas.txt" );int mi = 0 ;while ((mi=is.read())!=-1 ){char )mi);public static void main (String[] args) throws Exceptionnew FileInputStream("src/main/java/com/IO/dataTeas.txt" );byte [] by = new byte [3 ];int cnt = is.read(by);new String(by));new String(by));new String(by));new String(by));3 3 3 1 public static void main (String[] args) throws Exceptionnew FileInputStream("src/main/java/com/IO/dataTeas.txt" );byte [] by = new byte [3 ];int cnt = 0 ;while (( cnt = is.read(by)) != -1 ){new String(by,0 ,cnt));3 3 3 1
2.2 字节输出流(OutputStream)
FileOutputStream(String name):创建文件输出流以指定的名称写入文件。
FileOutputStream(String name, boolean append):创建文件输出流以指定的名称写入文件,append表示是否追加。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 new FileOutputStream("src/main/java/com/IO/dataTest.txt" );98 );'c' );'q' );new FileOutputStream("src/main/java/com/IO/dataTest.txt" );"qwertruyiop" ;new FileOutputStream("src/main/java/com/IO/dataTest.txt" ,true ); "qwertruyiop" ;
2.3 演示示例(复制功能) public static void main (String[] args) throws Exceptionnew FileInputStream("src/main/java/com/IO/binary.jpg" ); new FileOutputStream("src/main/java/com/IO/binary2.jpg" ); byte [] by = new byte [1024 ];int cnt = 0 ;while ((cnt = fis.read(by))!=-1 ){0 ,cnt);"OK" );
3.字节缓冲流
BufferedInputStream
public static void main (String[] args) throws Exceptionnew FileInputStream("src/main/java/com/IO/dataTest.txt" ); new BufferedInputStream(fis); int cnt = 0 ;while ((cnt = bis.read())!=-1 ){char )cnt);
BufferedOutputStream
public static void main (String[] args) throws Exceptionnew FileOutputStream("src/main/java/com/IO/dataTest3.txt" );new BufferedOutputStream(fos);"abcdef\r\n" ;for (int i = 1 ; i <= 3 ; ++i ){
4.序列化与反序列化 序列化是指把一个Java对象(类)变成二进制内容,本质上就是一个byte[]数组。反序列化,即把一个二进制内容(也就是byte[]数组)变回Java对象。
一个Java对象要能序列化,必须实现一个特殊的java.io.Serializable接口。Serializable接口没有定义任何方法,它是一个空接口。我们把这样的空接口称为“标记接口”(Marker Interface),实现了标记接口的类仅仅是给自身贴了个“标记”,表明可以序列化,其并没有增加任何方法。
4.1 序列化 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 package com.Serializable;import java.io.Serializable;public class Person implements Serializable public String name ;public int age ; public Person (String name, int age) this .name = name;this .age = age;public String getName () return name;public void setName (String name) this .name = name;public int getAge () return age;public void setAge (int age) this .age = age;@Override public String toString () return "Person{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +'}' ;public static void main (String[] args) throws Exceptionnew FileOutputStream("src/main/java/com/Serializable/test.bin" );new ObjectOutputStream(fos);new Person("zhangsan" ,23 );
4.2 反序列化 public static void main (String[] args) throws Exceptionnew FileInputStream("src/main/java/com/Serializable/test.bin" );new ObjectInputStream(fis);'zhangsan' , age=23 }
注意事项:
序列化类必须要实现Serializable接口。
序列化类中对象属性要求实现Serializable接口。
序列化版本号ID,保证序列化的类和反序列化的类是同一个类。
使用transient(瞬间)修饰属性,这个属性不能序列化。即不会保存。
静态属性不能序列化。即static修饰的。
序列化多个对象时,可以借助集合实现。
5.字符流 5.1 输入流(Reader) FileReader是Reader的一个子类,它可以打开文件并获取Reader。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 public static void main (String[] args) throws Exceptionnew FileReader("src/main/java/com/IO/dataTest.txt" );int cnt = 0 ;while ((cnt = fr.read())!=-1 ){char )cnt);public static void main (String[] args) throws Exceptionnew FileReader("src/main/java/com/IO/dataTest.txt" );char [] ca = new char [1024 ];int cnt = 0 ;while ((cnt = fr.read(ca))!=-1 ){new String(ca,0 ,cnt));
5.2 输出流(Writer) FileWriter就是向文件中写入字符流的Writer。它的使用方法和FileReader类似。
public static void main (String[] args) throws Exceptionnew FileWriter("src/main/java/com/IO/wdata.txt" );for ( int i = 1 ; i < 3 ; ++i){"这是一个写入样例" );"OK" );
5.3 演示示例(复制功能) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public static void main (String[] args) throws Exceptionnew FileReader("src/main/java/com/IO/wdata.txt" );new FileWriter("src/main/java/com/IO/wdata77.txt" );int cnt = 0 ;while ((cnt = fr.read()) != -1 ){"OK" );
6.字符缓冲流
BufferedReader
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 public static void main (String[] args) throws Exceptionnew FileReader("src/main/java/com/IO/wdata.txt" );new BufferedReader(fr);char [] ca = new char [1024 ];int cnt = 0 ;while ((cnt = br.read(ca))!=-1 ){new String(ca,0 ,cnt));public static void main (String[] args) throws Exceptionnew FileReader("src/main/java/com/IO/wdata.txt" );new BufferedReader(fr);null ;while ((st = br.readLine())!=null ){
BufferedWriter
public static void main (String[] args) throws Exceptionnew FileWriter("src/main/java/com/IO/wwdata.txt" );new BufferedWriter(fw);for (int i = 1 ; i < 5 ; ++i ){"好好学习,天天向上" );
7.打印流 PrintWriter 与 PrintStream 同样的用法。
public static void main (String[] args) throws Exceptionnew PrintWriter("src/main/java/com/IO/wwdata.txt" );23 );'v' );true );3.243 );23 true 3.243