本文最后更新于:December 3, 2021 pm
JAVA基础知识复习(八)。包装类、装箱拆箱。
目录
也可见 《JAVA基础知识复习(一)-正文》博客内容。
包装类(Wrapper)
针对八种基本数据类型定义相应的引用类型 — 包装类(封装类)。
| 基本数据类型 | 包装类 |
|---|
| byte | Byte | 父类 :Number |
| short | Short |
| int | Integer |
| long | Long |
| float | Float |
| double | Double |
| boolean | Boolean |
| char | Character |
基本数据类型转换为包装类
实例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| public class NewJavaTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i=120;
Integer ie = new Integer(i);
System.out.println(ie.toString());
Integer it = new Integer("12345");
System.out.println(it.toString());
}
}
120
12345
|
其他的类型用法同样的原理。
包装类转换为基本数据类型
实例:
| public class NewJavaTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer it = new Integer(13);
int i = it.intValue();
System.out.println(i+1);
}
}
14
|
基本数据类型、包装类转换成 String
由于基本数据类型与包装类之间可以自动转换,所以这里就把包装类和基本数据类型当成一种来和 String 之间进行转换。
方式一
| int num = 10;
String str = num + "";
10
|
方式二
| float fl = 12.3f;
double db = 23.5;
String str = String.valueOf(fl);
String str1 = String.valueOf(db);
System.out.println(str);
System.out.println(str1);
12.3
23.5
|
String 转换成基本数据类型、包装类
| public class NewJavaTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "234";
int num = Integer.parseInt(str);
System.out.println(num+1);
String str2 = "true";
boolean fl = Boolean.parseBoolean(str2);
System.out.println(fl);
}
}
235
true
|
转换图
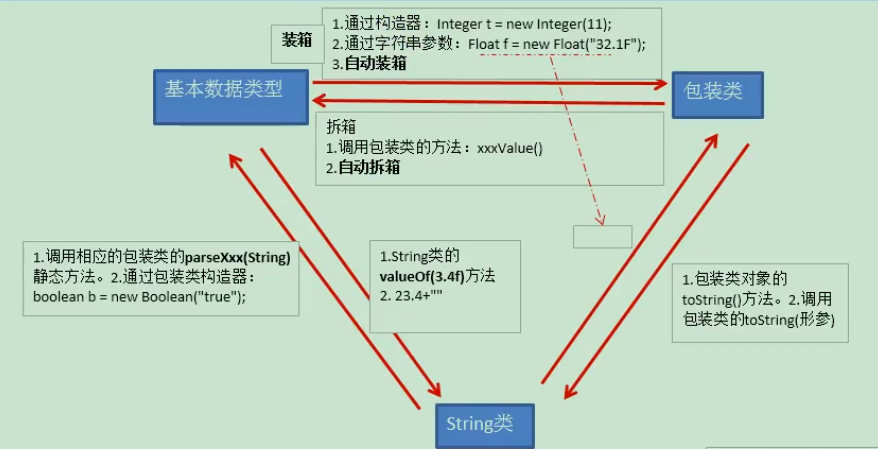
自动装箱
JDK 5.0 新特性。
基本数据类型转换成包装类。
可以理解成,小的转换成大的叫装箱。(这里的小、大表示的是谁包含谁)
实例:
| public class NewJavaTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num = 10;
Integer it = num;
System.out.println(it);
}
}
10
|
自动拆箱
包装类转换成基本数据类型。
可以理解成,大的转换成小的叫拆箱。(这里的小、大表示的是谁包含谁)
实例:
| public class NewJavaTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer it = 12;
int itt = it;
System.out.println(itt);
}
}
12
|

