本文最后更新于:April 4, 2022 pm
纸上得来终觉浅,绝知此事要躬行。路漫漫其修远兮,吾将上下而求索!知识是经过历史的巨人沉淀下来的,别总想着自己能够快速学会,多花点时间去看看,也许会发现些不同的东西。你能快速学会的、觉得简单的东西,对于别人来说也是一样的。人外有人,天外有天。当努力到达了一定的程度,幸运自会与你不期而遇。
目录 碰到了一个感觉可以用并查集解决的题,所以就复习一下普通并查集吧。因为学过也比较熟悉,所以本文主要是记录一下模板。
题目链接 (大致思路:从1开始,把经过的点都合并起来,最后看要求的点的根节点是否是1即可。AC代码见最后。)
并查集(Union-find Sets)是一种非常精巧而实用的数据结构,它主要用于处理一些不相交集合的合并问题。一些常见的用途有求连通子图、求最小生成树的 Kruskal 算法和求最近公共祖先(Least Common Ancestors, LCA)等。
它用于处理一些不交集的 合并 及 查询 问题。 它支持两种操作:
查找(Find):确定某个元素处于哪个子集;
合并(Union):将两个子集合并成一个集合。
在一些有N个元素的集合应用问题中,我们通常是在开始时让每个元素构成一个单元素的集合(即自己单独一个集合),然后按一定顺序将属于同一组的元素所在的集合合并,其间要反复查找一个元素在哪个集合中。
普通并查集模板 并查集(带路径压缩):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 static int [] par = new int [10005 ];public static void init (int n) for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) {public static int find (int x) if (par[x]!=x) par[x]=find(par[x]); return par[x];public static void unite (int x,int y) int tx = find(x);int ty = find(y);if (tx!=ty){
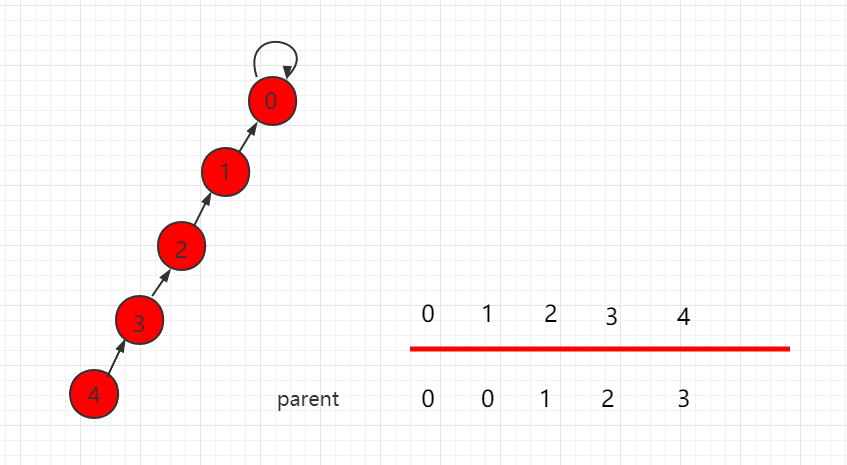
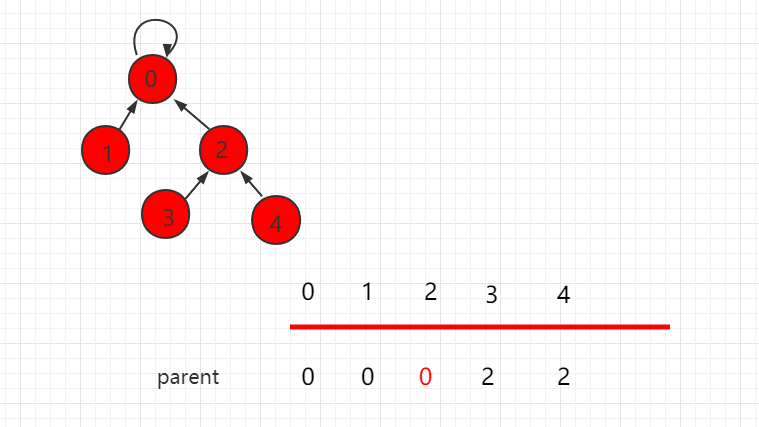
路径压缩理解:
从开始的这样
变成这样
再变成这样
最后变成了这样
维护集合中元素的个数 用来计算每一个集合中元素的个数有多少。在普通并查集的基础上加一个数组来统计每一个集合中元素的个数即可。在初始化的时候每一个集合中的个数都为1,在合并的时候将子节点中的元素个数加到根节点的元素个数中去。
就只是在普通并查集的基础上修改两个地方:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public static void init (int n) for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) {1 ; public static void unite (int x,int y) int tx = find(x);int ty = find(y);if (tx!=ty){
完整代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 static int [] par = new int [10005 ];static int [] sum = new int [10005 ];public static void init (int n) for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) {1 ;public static int find (int x) if (par[x]!=x) par[x]=find(par[x]); return par[x];public static void unite (int x,int y) int tx = find(x);int ty = find(y);if (tx!=ty){
维护节点到根节点的距离 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 import java.io.*;import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;import java.util.*;public class Main public static BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));public static BufferedWriter out = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));public static StreamTokenizer cin = new StreamTokenizer(new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)));public static PrintWriter cout = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));public static Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);public static int monthes[] = {0 , 31 , 28 , 31 , 30 , 31 , 30 , 31 , 31 , 30 , 31 , 30 , 31 };public static int maxd = 200000000 + 15 ;public static int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f ;public static int mod = (int ) 1e9 + 7 ;public static int [][] fx = {{1 , 0 }, {0 , 1 }, {-1 , 0 }, {0 , -1 }};public static int [] par = new int [maxd]; public static int [] dis = new int [maxd]; public static int find (int x) if (par[x]!=x){int t = par[x];return par[x];public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception int n = nextInt();for (int i=1 ;i<=n;++i) par[i] = i;for (int i=1 ;i<=n-1 ;++i){int x = nextInt();int y = nextInt();1 ; for (int i=1 ;i<=n;++i) {int p = find(i);" 到 " +p+" 的距离为:" +dis[i]);public static int gcd (int a, int b) while (b > 0 ) {return a;public static int log (int x) return (int ) (Math.log(x) / Math.log(2 ));public static void cinInit () 'a' , 'z' );'A' , 'Z' );128 + 32 , 255 );0 , ' ' );'/' );'"' );'\'' );public static int nextInt () throws Exception return (int ) cin.nval;public static long nextLong () throws Exception return (long ) cin.nval;public static double nextDouble () throws Exception return cin.nval;public static String nextString () throws Exception return cin.sval;public static void closeAll () throws Exception
AC代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 import javafx.util.Pair;import java.io.*;import java.text.DecimalFormat;import java.util.*;public class Main public static BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));public static BufferedWriter out = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));public static StreamTokenizer cin = new StreamTokenizer(new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)));public static PrintWriter cout = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));public static int [] par = new int [100005 ];public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception int n = (int ) cin.nval;int t = (int ) cin.nval;int [] f = new int [n + 5 ];for (int i = 1 ; i <= n - 1 ; ++i) {int ) cin.nval;for (int i=1 ;i<n;){int sm = i + f[i];if (sm<=n){if (par[t]==1 ){"YES" );else {"NO" );public static void init (int x) for (int i = 1 ; i <= x; ++i) {public static int find (int x) if (par[x] != x) par[x] = find(par[x]);return par[x];public static void unite (int x, int y) int tx = find(x);int ty = find(y);if (tx != ty) {public static void closeAll () throws Exception